I stumbled upon this website, https://www.w3resource.com/python-exercises/cybersecurity/, and found a bunch of cybersecurity puzzles to solve using Python. After tackling the first batch, I figured I'd share my solutions for the first 5 questions here.
Exercise 1:
The first challenge tasks us with creating a Python program that defines a function to hash a password string using SHA-256 and returns its hexadecimal representation. Utilizing the hashlib module, we encode the input text, compute its SHA-256 hash, and then convert it to a hexadecimal string.
import hashlib
def encrypt_str(text):
encrypted_text = hashlib.sha256(text).hexdigest()
print(f"Hashed value is: {encrypted_text}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
text_to_encrypt = str(input("Enter the text to hash: ")).encode('utf-8')
encrypt_str(text_to_encrypt)
Exercise 2:
In this task, we craft a Python program that defines a function to generate random passwords of a specified length. The function, gen_pass, utilizes the secrets module to create cryptographically secure random selections. By default, passwords are set to 8 characters in length but can be customized by the user. We ensure input validation, limiting the password length to less than 50 characters to maintain usability and security.
import string
import secrets
def gen_pass(size):
random_chars_gen = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
password = ''.join(secrets.choice(random_chars_gen) for i in range(size))
print(f"Random password of length {size}: {password}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
password_length = input("Enter the length of the password: ")
try:
if int(password_length) == 0:
password_length = 8
gen_pass(password_length)
elif int(password_length) > 0 and int(password_length) < 50:
gen_pass(password_length)
else:
print("Password length must be an integer less than 50. Generating passowrd with default value of 8.")
default_length = 8
gen_pass(default_length)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print("Password length must be an integer less than 50. Generating passowrd with default value of 8.")
default_length = 8
gen_pass(default_length)
Exercise 3:
In this task, we write a Python program to assess whether a password meets specific criteria. The criteria include being at least 8 characters long and containing at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one digit, and one special character (!, @, #, $, %, or &). Leveraging regular expressions, we validate the password's structure and characters, ensuring it meets the stipulated requirements. Upon evaluation, the program outputs a message indicating whether the password is valid or not.
import re
def check_pass(password):
valid_pass = False
string_check = True
special_chars = False
check_for_whitespace = bool(re.search(r"\s", password))
if len(password_to_test) < 8 or password.islower() or password.isupper() or password.isnumeric():
string_check = False
for i in password:
if i in ["!", "@", "#", "$", "%", "&"]:
special_chars = True
if string_check == True and special_chars == True and check_for_whitespace == False:
valid_pass = True
return valid_pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
password_to_test = input("Enter the password: ")
result = check_pass(password_to_test)
print(f"Password is valid: {result}")
Exercise 4:
This solution python function create_pass_sub, is to enhance password strength by suggesting common character substitutions. It iterates through the characters of the input password, identifying common substitutions. Substitutions such as replacing "s" with "$" or "i" with "!" are considered here but it can be further extended.
def create_pass_sub(password):
pass_options = []
for i in password:
if i in ["s", "5", "S"]:
pass_options.extend([password.replace("s", "$", 1), password.replace("5", "$", 1), password.replace("S", "$", 1)])
pass_options.extend([password.replace("s", "$"), password.replace("5", "$"), password.replace("S", "$")])
if i in ["i", "I", "1"]:
pass_options.extend([password.replace("i", "!", 1), password.replace("I", "!", 1), password.replace("1", "!", 1)])
pass_options.extend([password.replace("i", "!"), password.replace("I", "!"), password.replace("1", "!")])
return set(pass_options)
if __name__ == '__main__':
password_to_test = input("Enter the password: ")
result = create_pass_sub(password_to_test)
print("Password options:")
for x in result:
print(x)
Exercise 5:
This solution program reads a file containing a list of passwords, one per line. For each password, it checks if it meets certain requirements, such as being at least 8 characters long, containing both uppercase and lowercase letters, and having at least one number and one special character. The program utilizes regular expressions to validate the password structure and characters, ensuring they meet the specified criteria. Passwords that satisfy the requirements are printed by the program.
import re
def check_pass(password):
valid_pass = False
string_check = True
special_chars = False
check_for_whitespace = bool(re.search(r"\s", password))
if len(password_to_test) < 8 or password.islower == True or password.isupper == True or password.isnumeric == True:
string_check = False
for i in password:
if i in ["!", "@", "#", "$", "%", "&"]:
special_chars = True
if string_check == True and special_chars == True and check_for_whitespace == False:
valid_pass = True
return valid_pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
file_name = input("Enter filename with password(s): ")
try:
with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
password_to_test = line.strip()
print(f"Testing password: {password_to_test}")
result = check_pass(password_to_test)
print(f"Password is valid: {result}")
except Exception as e:
print(e)
Testing with a sample pass.txt as filename:
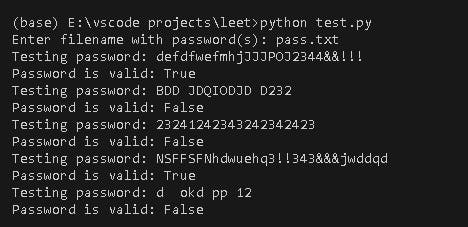
I found it quite enjoyable tackling these puzzles, and I urge you to give them a shot if you're interested.
Link to the puzzles: https://www.w3resource.com/python-exercises/cybersecurity/

